자료구조&알고리즘/C++
조합과 순열 4개중 2개 뽑기 예제코드
geminanolja
2025. 3. 3. 19:25
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm> // next_permutation 사용
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v = { 1, 2, 3, 4 }; // 예제 데이터
int cnt = 0;
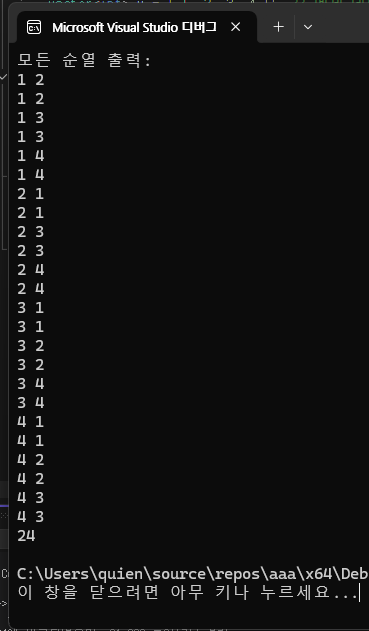
cout << "모든 순열 출력:" << endl;
do {
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) cout << v[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
cnt++;
//cout << cnt;
} while (next_permutation(v.begin(), v.end())); // 다음 순열 생성
cout << cnt << endl;
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm> // next_permutation 사용
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n = 4, r = 2; // 4개 중에서 2개 선택
vector<int> combination(n, 0);
fill(combination.end() - r, combination.end(), 1); // 마지막 r개만 1로 설정
vector<int> elements = { 1, 2, 3, 4 }; // 조합을 만들 원소들
cout << "모든 조합 출력:" << endl;
do {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (combination[i]) cout << elements[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
} while (next_permutation(combination.begin(), combination.end()));
return 0;
}
- 첫 번째 코드: 순열 (Permutation) → 순서가 중요
- 두 번째 코드: 조합 (Combination) → 순서가 중요하지 않음
✅ 1️⃣ 첫 번째 코드 (순열) 실행 결과 검증
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm> // next_permutation 사용
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v = { 1, 2, 3, 4 }; // 예제 데이터
int cnt = 0;
cout << "모든 순열 출력:" << endl;
do {
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) cout << v[i] << " "; // 앞의 2개만 출력
cout << endl;
cnt++;
} while (next_permutation(v.begin(), v.end())); // 다음 순열 생성
cout << "총 개수: " << cnt << endl;
return 0;
}
🟢 [순열 결과]
경우의 수 출력 값
| 1️⃣ | 1 2 |
| 2️⃣ | 1 3 |
| 3️⃣ | 1 4 |
| 4️⃣ | 2 1 |
| 5️⃣ | 2 3 |
| 6️⃣ | 2 4 |
| 7️⃣ | 3 1 |
| 8️⃣ | 3 2 |
| 9️⃣ | 3 4 |
| 🔟 | 4 1 |
| 11️⃣ | 4 2 |
| 12️⃣ | 4 3 |
➡ 총 개수 = 4P2 = 4! / (4-2)! = 4 × 3 = 12 (✅ 정답!)
✔ 결과적으로, "4개 중 2개를 순서 있게 뽑는 경우"가 맞다.
✔ next_permutation()을 사용하여 2개씩 출력했기 때문에 올바른 순열을 생성한다.
✔ 순서가 다르면 다른 경우로 처리되므로 순열이 맞다.
✅ 2️⃣ 두 번째 코드 (조합) 실행 결과 검증
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm> // next_permutation 사용
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n = 4, r = 2; // 4개 중에서 2개 선택
vector<int> combination(n, 0);
fill(combination.end() - r, combination.end(), 1); // 마지막 r개만 1로 설정
vector<int> elements = { 1, 2, 3, 4 }; // 조합을 만들 원소들
cout << "모든 조합 출력:" << endl;
do {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (combination[i]) cout << elements[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
} while (next_permutation(combination.begin(), combination.end()));
return 0;
}
🔵 [조합 결과]
경우의 수 출력 값
| 1️⃣ | 1 2 |
| 2️⃣ | 1 3 |
| 3️⃣ | 1 4 |
| 4️⃣ | 2 3 |
| 5️⃣ | 2 4 |
| 6️⃣ | 3 4 |
➡ 총 개수 = 4C2 = 4! / (2!(4-2)!) = 6 (✅ 정답!)
✔ "4개 중 2개를 순서 상관없이 뽑는 경우"가 맞다.
✔ (1,2)와 (2,1)이 같은 것으로 처리되므로 조합이 맞다.
✔ next_permutation()을 사용하여 1과 0의 조합을 변환하며 모든 경우를 탐색한다.
🔍 결론 (🚀 두 코드 모두 올바르게 동작함!)
코드 개수 특징 결과 검증
| 순열 (Permutation) | 12 | 순서 O | ✅ 4P2 = 12 정확함 |
| 조합 (Combination) | 6 | 순서 X | ✅ 4C2 = 6 정확함 |